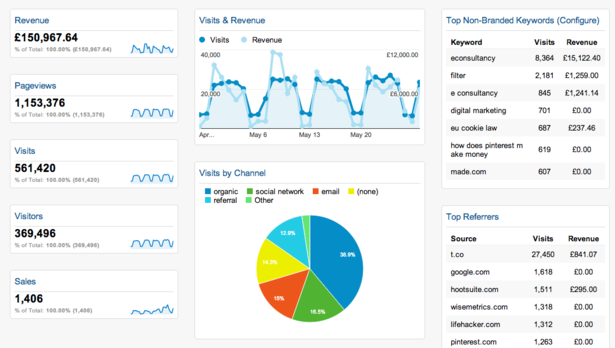
Google Analytics is one of the dynamic tools used for analyzing the improvement and performance of your websites. It is fully equipped with high-tech tools and features that can really develop the efficiency of your online marketing. However, the information might be easy to get hold of, but it doesn’t make it stress-free to understand and make strategies for new comers. To assist learners here is the essential key points you may come across when navigating through Google analytics.
Page views: This is the number of times customers visit a page that has Google Analytics tracking code inserted. Page view is defined as an interpretation of a page on your site that is being pursued by the Google Analytics. It is a count of viewed pages and not individual visitors. If a customer refreshes a page, or navigate away from the page and returns, these are calculated as additional page views. This assists you to identify your most popular pages.
Visits/Sessions: Visits are individual’s periods of time or sessions that audiences spend on your website. There are different ways to count the visit session and this can be tracked with the help of Google Analytics. When individual visits the site either for 30 minutes, more than 30 minutes or return the website within 30 minutes is treated as original visits.
Unique Page views: The unique page view is a total of all the times the pages was viewed in an individual session as a single event. If an audience viewed the page once in a visit or three times, the number of unique page views will be calculated as just one.
Unique Visitor: When a consumer visits your website for the first time, new visit and unique visitor both are recorded. The Analytics track can analyze the difference of same visitor visiting the site after the initial visit and new visitors. If the same visitors are visiting the site again and again then only a new visit is added and not recorded as unique visitors. But at the same time if a user deletes their cookies, history and access the sites through different browser or appliances then they may considered as new unique visitor.
Hits: Hits are the connections during a visit, comprising page views, events and transactions.
New Vs Returning Visitors: The Analytics keep the track record of new and returning visitors. With the help of these records you can differentiate the new and returning visitors. New visitors are counted as those users that have not yet visited the website and returning visitors are considered as those visitors who have visited the website at least once in a time period. Google Analytics use cookies to identify earlier visits.
Segments: According to your own specific requirement, Google Analytics permits you to make subcategories of your data. Segments facilitate you to analyze data in more aspects by filtering the results to reveals only statistics for certain types of traffic. Segments can be used to compare results between groups of visitors. For example: paid vs organic search traffic. Custom segments can be setup to analyze data more accurately.
Entrances: Entrance signifies the number of visits that occurs on a particular web page or group of web pages.
Bounce rate: The bounce rate is measured in percentage. A Bounce signifies a visit with just a single page view. It signifies the number of visits when consumers go away from your site after just one page view, irrespective of how long they stayed on that page.
Time on Page: Time on page defines the average amount of time in seconds an audience spends on a single page. Technically it defines the starting time of the given page view and subsequent page views or event.
Content: The Google Analytics also helps you to check which piece of content visitor visited you site.
Direct Traffic and Referral Traffic: Google Traffic sources reveal how consumers visited to your site. Traffic sources divided into direct and referral traffic. Direct traffic is known when visitors type a URL or click on bookmark to visit to your site. Referral traffic is when a consumer has landed on your site by clicking on a URL from somewhere else; it could be anything such as social media, search engine or another website.
Organic Search Traffic and Paid Search Traffic: Google Analytics allows you to analyze what percentage of your traffic came from search engine. It divides into organic and paid search. In organic search traffic, visitors come to your website by clicking on organic links through search engine result pages. It is easy to check these results below search engine result page (SERP) and are determined by how well the page is optimized for search engines. The paid search results displace consumers who clicked on your paid search engine advertisements. These paid results can be seen either at the top and side of the SERP and are organized by a PPC specialist who manages Google Adwords or Bing Ads.
Events: Events characterize custom actions that are distinctive to a particular Google Analytics account. Events can comprise actions like clicking hyperlinks, images or stop and play buttons in video players. These can be set up to help you track activity of page or screen loads.
Goals: Goals can be structured in Google Analytics account to analyze the conversion rate of the various activities by the audiences on your site. These actions may comprise a visitor making a purchase, finishing a game, downloading an ebook or signing up for email newsletter. You can also give a monetary value to each goal completion to check the return on investment from your website.
It’s significant to note that this is not a complete range of all Google Analytics key terms, but these are the key terms in Google Analytics which offers information to new users or a reminder for those with more experience.